
An integral part of any electric grid are its electrical transformers. As the name implies, the role of transformer cores is to convert or “transform” incoming voltage into a desirable outgoing voltage. The energy may be stepped up to higher voltages or stepped down to lower voltages. An example of when energy would need to be stepped up is when it’s going to travel long distances, as this increases the efficiency.
Then, as the energy goes from the power lines into residential homes, it would be stepped down before going into the breaker box. To accomplish these tasks, electric transformers can be as large as buildings or as small as cellphones.
Different parts of an electrical transformer are made of different materials. Windings are usually made of copper or aluminum, while the laminations are made of steel, often silicon steel. Cores can also be made of iron, amorphous metals, and ferrite ceramics, among others.
About Transformers: The Core
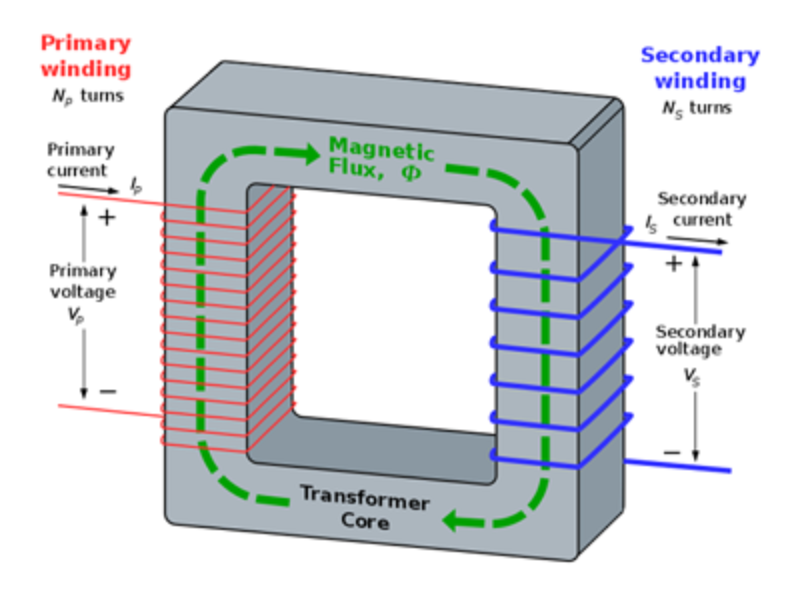
The center of a transformer is called the core. Here, the electricity flows through a primary winding creating a magnetic flux. As the magnetic field cuts through the secondary winding, the secondary winding picks up the voltage. The power is stepped-up or down in relation to the amount of turns of each winding. More turns on the secondary winding, and the voltage increases. Less turns, and it decreases.
More About Transformer Cores: Types of Transformer Cores
The two primary types of transformer cores are shell type and core type. In shell type cores, the cores surround the winding. In contrast, core type is characterized by the windings surrounding the core, as can be seen in the graphic below.
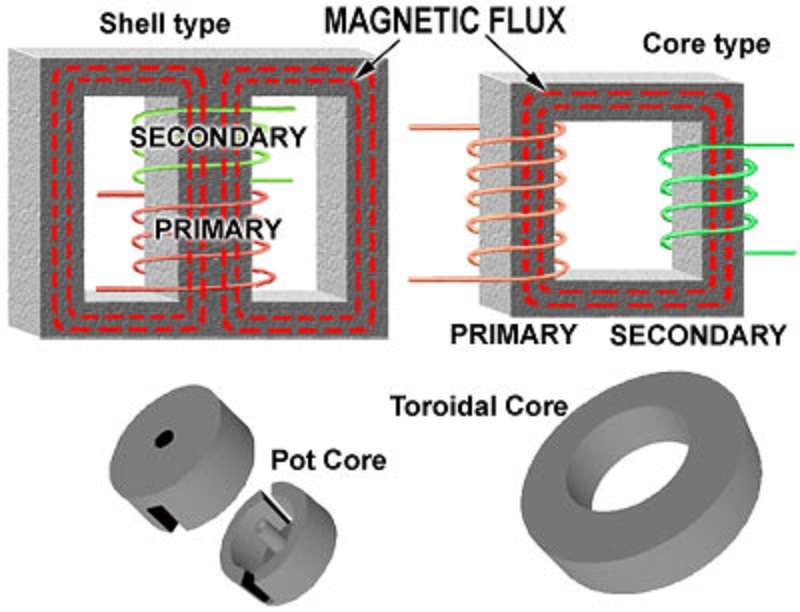
Core type configurations are used for high voltage/high power needs. Although their power losses tend to be higher, the windings in core type are readily available and so maintenance is easier than in shell type transformers. Finally, because in core type transformers the windings are placed on separate legs, more copper is required in the manufacturing of core type transformers.
On the other hand, shell type cores are used for lower power applications. They have less energy losses, but maintenance is harder because the windings are harder to reach. The better energy containment is due to the windings being closer to each other and the magnetic flux having a closed path around the coils on which to travel. In contrast to the core type, shell type transformers allow for natural cooling. The mechanical strength of shell type transformers is also higher.
About Transformer Cores: Transformer Core Manufacturing
The coupling, or electromagnetic connection between the two windings, must be set up well to prevent loss. In addition, the layers of steel that make up the core’s structure should be as permeable as possible to conduct the magnetic flux from one winding to the other. Stacking layers of thin lamination, rather than a core built from one solid piece, has the effect of reducing eddy currents and heating.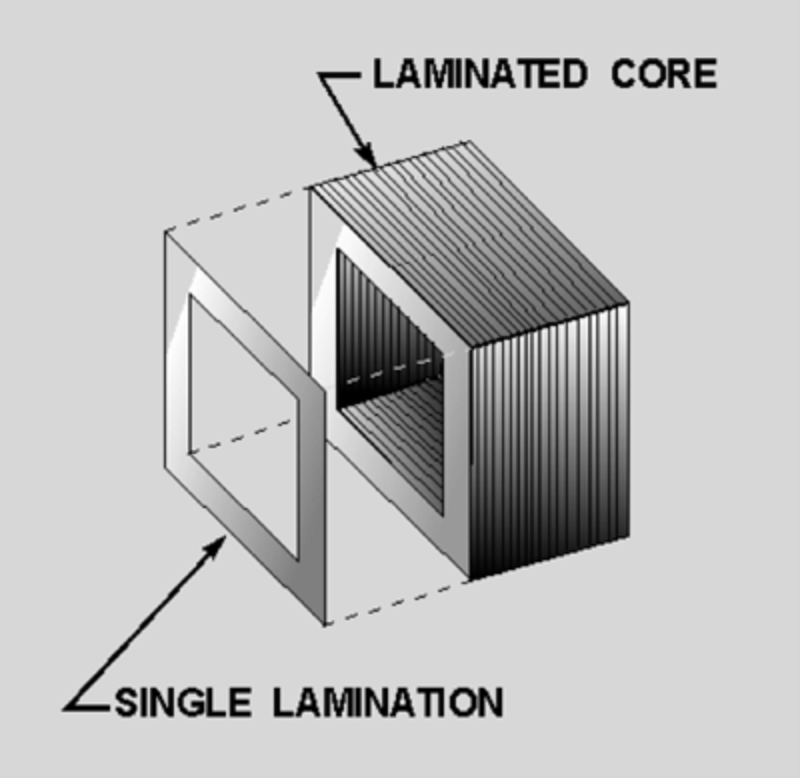 As efficiency regulations become stricter, demand increases for conventional grain-oriented and high permeability electrical steels, and worldwide strategic sourcing becomes fundamental. To meet these demands, Hunan Hongwang has provides CRGO, high-grade NOES and HiB GOES, welcome your inquiry!
As efficiency regulations become stricter, demand increases for conventional grain-oriented and high permeability electrical steels, and worldwide strategic sourcing becomes fundamental. To meet these demands, Hunan Hongwang has provides CRGO, high-grade NOES and HiB GOES, welcome your inquiry!
Current situation and future development trend of Chinese automotive motor iron core market
2024-01-18Technical Solutions for Core Materials and Lightweight Transformer Design
2025-01-04Indonesia Nickel Production NOT Affected by Earthquake
2021-01-11Iron core soft magnetic materials can actually do thermoelectric materials
2024-05-31What is duplex stainless steel and why so many person are concerned of S32001 duplex ?
2022-07-18Development trend and enlightenment of electrical steel industry
2024-02-28






