
In an electric motor, the stator and rotor are essential components. The stator is fixed to the housing and usually has a coil wound around the stator. The rotor is mounted on the frame by bearing or bushing. The rotor is fitted with silicon steel sheets and coils. When an electric current passes through the coil, a magnetic field is generated on the silicon steel sheet of the stator and rotor, which drives the rotating motion of the rotor.
The stator of asynchronous motor is composed of stator core, stator winding and frame. The stator core is a part of the magnetic circuit of the motor, which is used to insert the stator winding and provide the magnetic path. It is composed of multiple layers of 0.5mm thick silicon steel sheet laminated, and the insulating paint is applied between the sheets to ensure mutual insulation, thereby reducing the core loss of the rotating magnetic field on the stator core. The stator core inner punch has a plurality of identical slots for installing the stator windings. The stator winding is the circuit part of the motor, and its main function is to carry on the current and generate the induced potential, so as to realize the conversion of electrical energy to mechanical energy. The stator winding coil is distributed in the stator slot and can be divided into two structures: single layer and double layer. In order to obtain good electromagnetic properties, medium and large asynchronous motors usually use double-layer short-distance winding. The main role of the stator frame is to fix and support the stator core, so it needs to have enough mechanical strength and stiffness to withstand various forces during motor operation or transportation. Small and medium-sized AC motors usually use cast iron frames, and for larger capacity AC motors, steel plate welding frames are generally used.
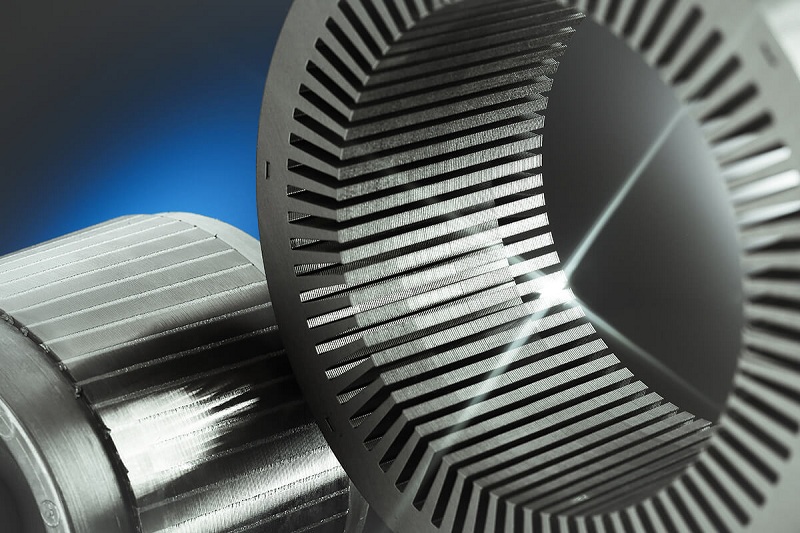
The rotor core is a part of the magnetic circuit of the motor, and the stator core and the air gap together form the magnetic circuit of the whole motor. The rotor core is usually composed of multiple layers of 0.5mm thick silicon steel sheets laminated. The rotor core of small and medium-sized AC motors is usually installed directly on the motor shaft, while the rotor core of large AC motors is installed on the rotor bracket, which in turn is placed on the rotating shaft. The role of rotor winding is to induce potential, flow current and generate electromagnetic torque, its structure usually has two kinds of squirrel-cage type and winding type.
The squirrel cage rotor winding is a self-closing winding. A guide bar is inserted into each slot, and at the notches at both ends of the core, there are two end rings that connect the two ends of all the guide bars respectively. If the core is removed, the shape of the entire winding is like a "round cage", so it is called a squirrel cage rotor.
The wound rotor winding is similar to the stator winding, using insulated wires embedded in the rotor core slot and connected into a star-shaped three-phase symmetrical winding. Then, the three small wire ends are connected to the three collector rings on the rotor shaft, and the current is drawn through the brush. The characteristic of the wound rotor is that external resistance can be inserted into the rotor winding loop through the collector ring and brush to improve the starting performance of the motor or adjust the speed. In order to reduce brush wear, linear induction motors are sometimes equipped with brush shorting devices, when the motor is started and does not need to adjust the speed, the brush can be lifted and the three collector rings are shorted at the same time.
Cold rolling process of stainless steel
2023-09-28Transformer Core Loss Optimization Design and Energy-Saving Technology Discussion
2024-12-17UP RMB50? China 201 Stainless Steel Market Counterattack Again
2020-11-25High grade eletrical steel material or usher in structural prosperity
2023-09-07How to "solve" the iron core loss of electric drive?
2024-07-04Analysis of the Impact of Core Flux Density Distribution on Transformer Performance
2025-01-21






