
Current Location : Home > News > Industry News > How to "solve" the core loss of electric drive?
How to "solve" the core loss of electric drive?
Time:2024-06-24
Source:
Hits:590
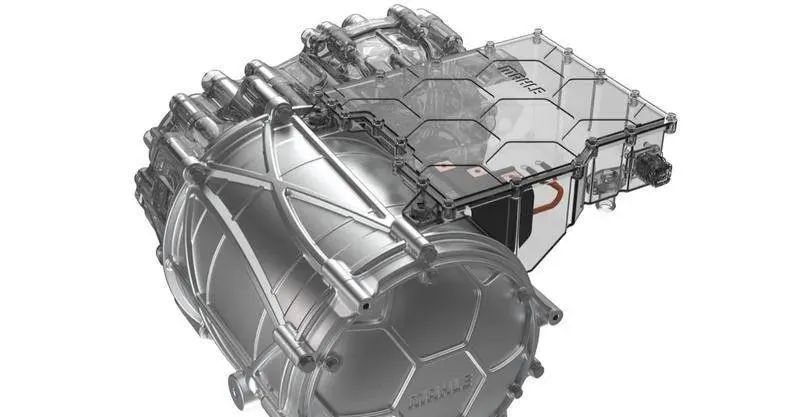
For people engaged in motor manufacturing, electrical steel sheet is a common material. It also has many other names, such as silicon steel sheet, silicon steel sheet, punching, lamination and so on. With the development of electric vehicles, higher requirements are put forward for motor performance, and high energy efficiency and high power density are becoming more and more important. The design of the motor core is one of the important factors.
There are two important loss sources in the core, hysteresis loss and eddy current loss, and both of these losses increase with the increase of the motor frequency (hysteresis loss is proportional to the frequency, eddy current loss is proportional to the square of the frequency). In the pursuit of high motor speed today, how to reduce these two losses is a key issue to consider.

Hysteresis loss refers to the energy consumed due to hysteresis in the process of repeated magnetization of ferromagnetic materials. Hysteresis phenomenon means that when the magnetic state of the ferromagnetic material changes, the magnetization lags behind the magnetic field strength, that is, the relationship between the magnetic flux density B and the magnetic field strength H shows hysteresis loop. During each magnetization cycle, the hysteresis loss per unit volume of the core is proportional to the area of the hysteresis loop. This part of the energy will be converted into heat, resulting in equipment temperature rise and efficiency reduction. Hysteresis loss is an important part of iron loss in electrical equipment, and in equipment such as AC motors, we want to minimize the impact of hysteresis loss.
At present, it is possible to improve the performance of various types of motors by optimizing silicon steel sheets. This is because the key task of the motor is to use the magnetic induction line generated by the permanent magnet to cut the silicon steel sheet, but once the magnetic field is closed inside the iron core, it will generate eddy currents and generate heat, which is equivalent to a waste of energy. This is also a source of iron damage. However, there is a tradeoff point in motor design where the edge portion of the bound permanent magnet can adopt a narrower width for higher flux saturation and better magnetic field effects. But if the design is too narrow, this can lead to a loss of strength.
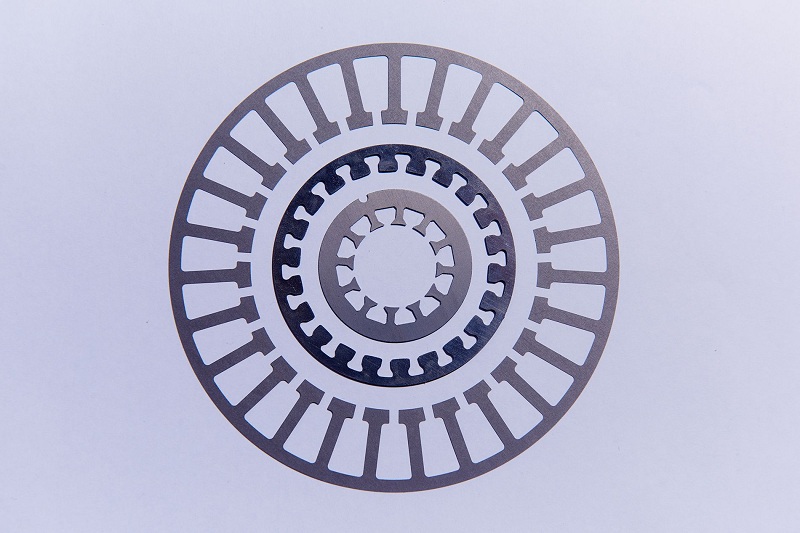
Eddy current means that when the current in one coil changes with time, an induced current is generated in another coil nearby due to the action of electromagnetic induction. This explanation is quoted from Baidu, but is not directly related to the eddy current in the core we mentioned in our discussion. This explanation mainly involves vortices in the wire, not in the magnetic core. In fact, the vortex in the core refers to the circulation formed inside the core. According to the right hand rule, the direction of the magnetic field can be determined when the current passes through the winding, usually in a clockwise direction. In the cross section of the magnetic core, according to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction (the area of the closed coil is unchanged, changing the magnetic field strength will lead to a change in the magnetic flux), according to Lenz's law, we know that there will be a counterclockwise vortex at the right section, generating a reverse magnetic field to offset this change.
In order to ensure the strength of the magnetic core, many automobile manufacturing companies have adopted a new type of adhesive technology to make silicon steel sheets. This technology can not only improve the structural strength of the magnetic core, but also solve the problem of eddy current loss, the second type of iron loss. The generation of eddy current loss is easy to understand, when the conductor is moving in a non-uniform magnetic field or in a magnetic field that changes with time, the current induced in the conductor will cause the conversion of energy and generate heat. Many previous motors used a lamination form similar to a mortise and tenon structure, where the protrusions on both sides caused vortices throughout the rotor section. However, most motors now use a new type of gluing so that there is no need to create protrusions on the chip.
The motor rotor is not made of a single iron ingot, but of a very thin sheet of silicon steel stacked on top of each other. In principle, the motor rotor market is a huge new blue ocean that cannot be filled even if suppliers go all out. Such a good market is extremely scarce, and even shows the trend of monopoly. The reason is that there are not many high-end manufacturers. In retrospect, foreign companies such as France's Bulgari Steel, Italy's EURO Group and Japan's Kuroda have very limited help in the development of the domestic new energy industry chain, so we must support domestic enterprises. Because the connection process of the core silicon steel sheet is the key of the motor.
Related News
Punching technical requirements for iron core
2024-01-04Stainless steel surface treatment process- beadblasting
2020-10-20What is Titanium Grade1 and how does it differ?
2026-01-08Analysis of transformer import volume in future transformer manufacturing industry
2023-08-28Brief classification of silicon steel
2022-09-09Where is the application field of 316L stainless steel pipe drawing technology?
2021-03-10






